Setting a TTL (Time-to-Live) on Your Simulations
The Challenge
When running simulations, it’s important to control how long a task can run to avoid unnecessary resource usage and costs. Without limits, tasks may run longer than expected, leading to wasted time and compute resources.
The Solution
To set a TTL (Time-to-Live) for your simulation, use the time_to_live parameter when
submitting the task. This parameter defines the maximum duration the task is allowed to
run, specified as a string duration. It supports common time formats such as “10m”,
“2 hours”, “2h”, “1h30m”, or “90s” (see
here
for more details on supported formats). The task will be automatically terminated if it
exceeds this duration after starting. This feature helps you control resource usage and
avoid running tasks longer than necessary (e.g., perfect for quick test runs).
import inductiva
# ...
task = simulator.run(
input_dir=input_dir,
on=cloud_machine,
time_to_live="1m", # Sets TTL to 1 minute
)
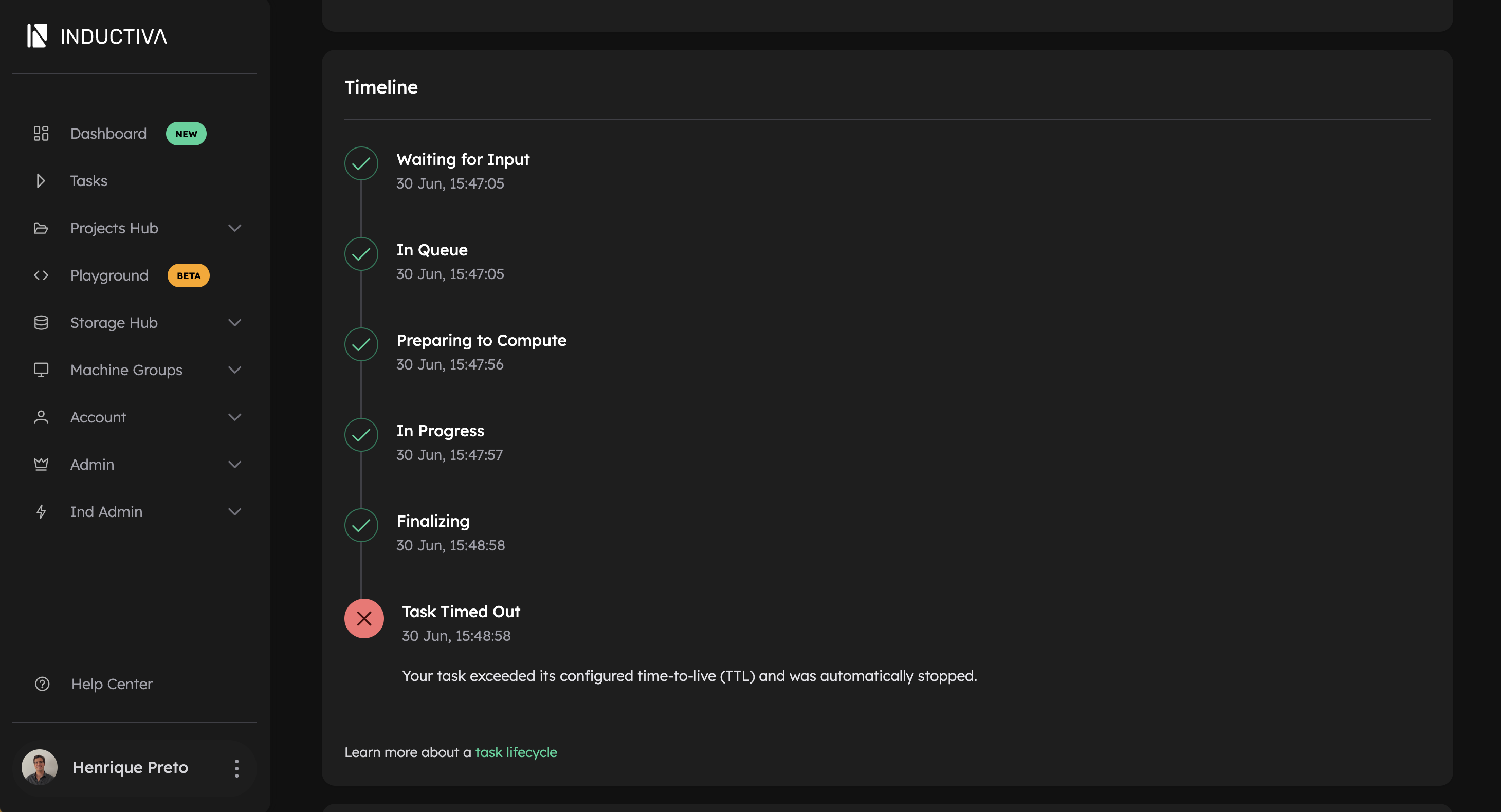
If the simulation exceeds the maximum duration (in this case, 1 minute), you’ll see logs like these in your terminal indicating that it was automatically terminated because the TTL was reached:
■ Your task exceeded its configured time-to-live (TTL) and was automatically stopped.
Downloading stdout and stderr files to inductiva_output/h04n8swuji8jgrex5sq7smsg2/outputs...
Partial download completed to inductiva_output/h04n8swuji8jgrex5sq7smsg2/outputs.
In the Inductiva Console, open the Tasks tab and click on your task to view its details. You’ll see something like this: