From your laptop to large-scale simulations with five lines of Python.
Manage Resources
Once you have created your resources, the Inductiva API provides various methods and tools for managing them. This guide covers everything from launching resources to monitoring costs and terminating them when you're done.
For consistency, our examples will primarily use the MachineGroup class. However, these methods are universal and work identically for both ElasticMachineGroup and MPICluster resources.
Quick Start
The typical workflow for managing computational resources follows three simple steps:
- Start resources when you need to run simulations
- Monitor them while they're running
- Terminate them when you're done to avoid unnecessary costs
import inductiva
# 1. Start computational resources
machine_group = inductiva.resources.MachineGroup(
machine_type="c2-standard-4", # Choose appropriate machine type
num_machines=2, # Scale based on your workload
data_disk_gb=100, # Enough storage for your data
spot=True # Save costs by using spot machines
)
machine_group.start()
# 2. Monitor your resources
resources = inductiva.resources.machine_groups.get()
print(f"Active resources: {len(resources)}")
# For example, fetch the estimated cost
cost = machine_group.estimate_cloud_cost()
print(f"Current resource cost: ${cost:.2f}/hour")
# 3. Always terminate when done
machine_group.terminate()
💡 Pro tip: Resources continue charging until terminated, so always clean up when finished! Don't worry if you forget -- we have a background monitoring service that automatically terminates idle machines.
Core Operations
Start
Start computational resources to run your simulations. You can start resources using Python or the CLI.
Python
# Create and start a machine group
machine_group = inductiva.resources.MachineGroup(
machine_type="c2-standard-4",
num_machines=4,
disk_size_gb=50,
spot=True
)
machine_group.start()
CLI
inductiva resources start c2-standard-4
Or start with specific options:
inductiva resources start c2-standard-4 \
--n 4 \
-d 50 \
--s
Run
inductiva resources start --helpto see the full command syntax, arguments and options
List
List and check the details of your active resources.
Python
## Obtain a list with instances of all active resources
>>> resources_list = inductiva.resources.machine_groups.get()
>>> print(resources_list)
[MPICluster(name="api-23zssj6oq77xxsot3o0nhax3d"),
ElasticMachineGroup(name="api-45fetsr58okcs0x6j9m0vsi2z"),
MachineGroup(name="api-4kken08fnoxuu5zjjak6ak2xe")]
CLI
inductiva resources list
One obtains for example the following output:
Active Resources:
NAME MACHINE TYPE ELASTIC TYPE # MACHINES DATA SIZE IN GB SPOT STARTED AT (UTC) IDLE TIME MAX COST ($/HOUR)
api-3ejvh64mxuxnfcv3yxdhoyjuj c2-standard-4 False standard 5/5 50 False 10 Jul, 16:23:00 0:01:15/0:3:00 1.4909
api-5014txg0rwx3jbbpf6y0ndzmv c2d-highmem-16 False mpi 3/3 10 False 10 Jul, 16:22:04 0:02:12/0:3:00 3.27774
api-es9sjockjymvkwfmjioibfw8p c2-standard-8 False standard 2/2 60 False 10 Jul, 16:23:25 0:02:50/0:03:00 1.08312
.. seealso::
Run `inductiva resources list --help` to see the full command syntax, arguments and options
Web Console
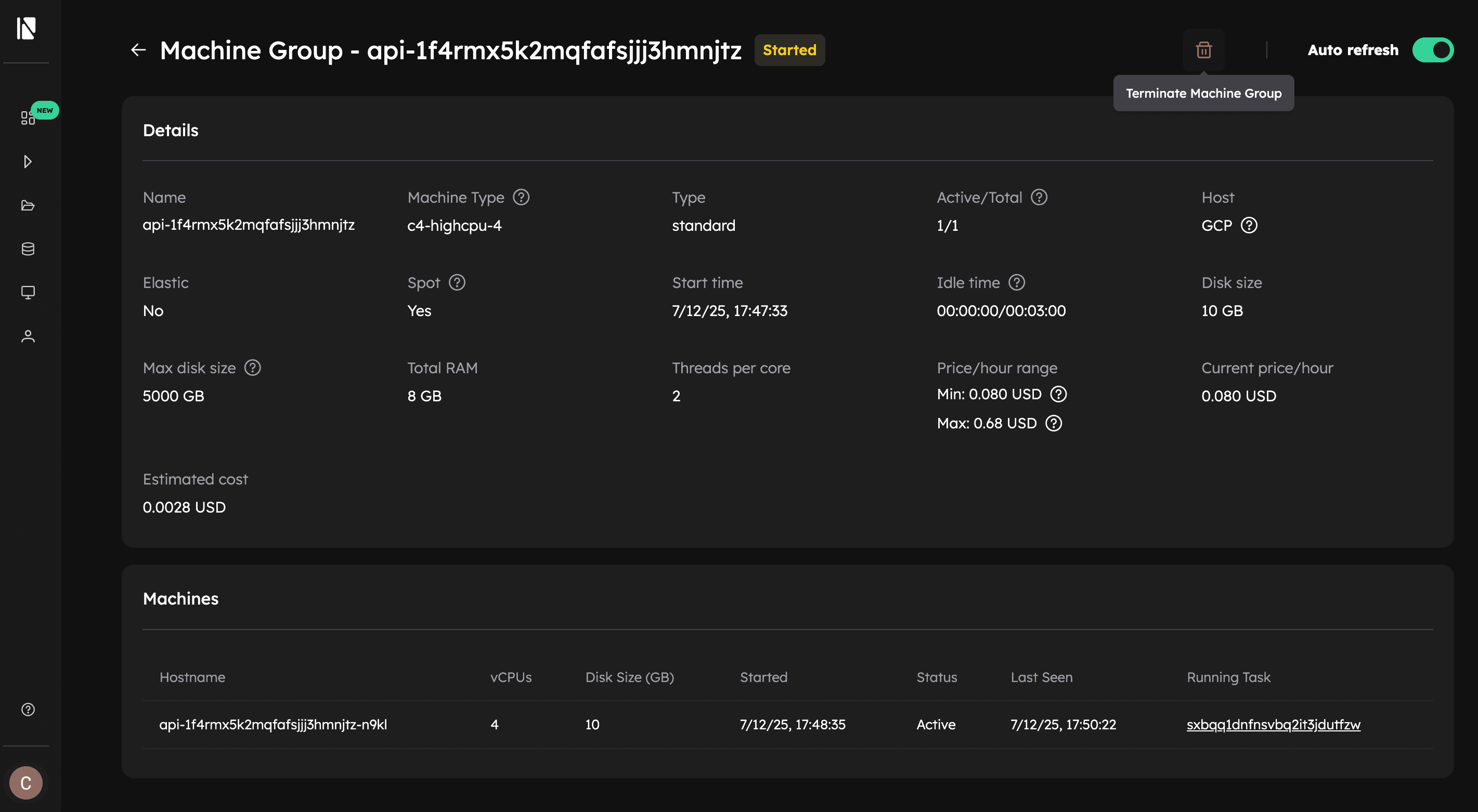
From Inductiva's Web Console, you can also view your active resources navigating to the dedicated Active Machine Groups page.
Monitor Costs
Keep track of your resource costs to optimize your spending.
Python
When you register a resource object using the Python API, you can view the estimated cost in the CLI logs:
■ Registering MachineGroup configurations:
· Name: api-2tq6za9oo7i9dym4o5049wu5f
· Provider: GCP
· Machine Type: c4-highcpu-4
· Data disk size: 10 GB
· Auto resize disk max size: 5000 GB
· Total memory (RAM): 8 GB
· Maximum idle time: 3 minutes
· Auto terminate timestamp: N/A
· Number of machines: 1
· Spot: True
· Estimated cloud cost of machine group:
· Minimum: 0.080 $/h (1 machine with 10 GB disk)
· Maximum: 0.690 $/h (1 machine with 5000 GB disk)
· You are spending 2.4x less by using spot machines.
You can later also fetch this cost value again:
>>> cost_estimate = machine_group.estimate_cloud_cost()
>>> print(f"Current resource cost: ${cost_estimate:.2f}/hour")
Current resource cost: $0.65/hour
CLI You can check the cost for a specific configuration
inductiva resources cost c2-standard-4
# Output: Estimated total cost (per machine): 0.23 US$/h
.. seealso::
Run `inductiva resources cost --help` to see the full command syntax, arguments and options
Web Console
- Navigate to the Active resources page.
- Click on the resource and see the value under Estimated Cost.
Or you can see the cost of a terminated resource:
- Navigate to the Terminated resources page.
- Click on the resource and see the value under Cost.
Terminate
Stop your resources when you're finished to avoid unnecessary costs.
Python
# Terminate a specific resource
machine_group.terminate()
# Terminate by name
inductiva.resources.machine_groups.get_by_name("api-45fetsr58okcs0x6j9m0vsi2z").terminate()
# Get and terminate all resources
resources = inductiva.resources.machine_groups.get()
for resource in resources:
resource.terminate()
CLI
# Terminate a specific resource (requires confirmation)
inductiva resources terminate api-45fetsr58okcs0x6j9m0vsi2z
# Terminate all resources (requires confirmation)
inductiva resources terminate --all
Web Console
- Navigate to the Active resources page.
- Click on the resource you want to terminate and click the Terminate Machine Group button.
All these are a blocking call that will only finish when the machines have terminated, in this way no computational resources are left up.